In recent decades, road safety has shifted from reactive measures to proactive technologies designed to prevent crashes before they occur. This transformation is largely thanks to a host of inventions developed by pioneering engineers, automotive giants, and innovative startups. Here’s a timeline of some of the most influential devices and technologies created to reduce traffic accidents—and the inventors and companies behind them.
Vehicle-Based Safety Technologies
1. Crumple Zones (1959) 
-
-
Inventor: Béla Barényi
-
Manufacturer: Mercedes-Benz
-
Purpose: Designed to absorb impact energy during collisions, protecting occupants by deforming in a controlled manner.
-
Crumple zones, introduced in 1959 by the innovative engineer Béla Barényi while working for Mercedes-Benz, revolutionized automotive safety. These zones are strategically designed areas of a vehicle that deform in a controlled manner during a collision. By absorbing and dissipating impact energy, crumple zones significantly reduce the force transferred to the vehicle’s occupants, thereby enhancing passenger safety. Barényi’s pioneering concept marked a fundamental shift in car design, moving away from prioritizing the vehicle’s integrity to focusing on passenger protection. The widespread adoption of crumple zones in modern vehicles underscores their critical role in reducing injuries and saving lives on the road.
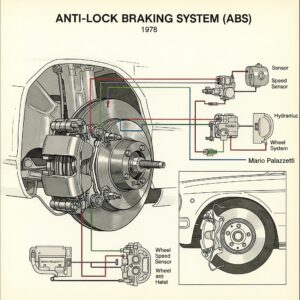
2. Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) (1978)
-
-
Inventor: Mario Palazzetti
-
Manufacturer: Bosch (in partnership with Daimler-Benz)
-
Purpose: Prevents wheel lock-up during emergency braking, improving steering control.
-
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), invented by Mario Palazzetti and first introduced in 1978, represents a significant advancement in automotive safety technology. Developed in partnership between Bosch and Daimler-Benz, ABS is designed to prevent the wheels of a vehicle from locking up during emergency braking situations. This innovation enhances vehicle control and reduces stopping distances on slippery surfaces, thereby improving the driver’s ability to maintain steering control during critical moments. By pulsating brake pressure to each wheel individually, ABS helps to prevent skidding and allows drivers to steer around obstacles more effectively. This system has since become a standard feature in modern vehicles, underscoring its importance in enhancing road safety and driver confidence.
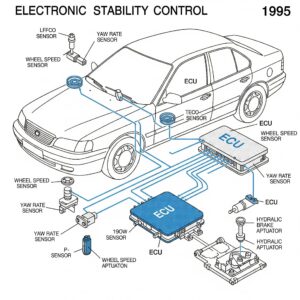
3. Electronic Stability Control (ESC) (1995)
-
-
Developer: Mercedes-Benz and Bosch
-
Purpose: Automatically applies brakes to individual wheels to help drivers maintain control during skids.
-
Electronic Stability Control (ESC), developed collaboratively by Mercedes-Benz and Bosch in 1995, represents a significant advancement in automotive safety technology. Its primary purpose is to enhance vehicle stability by automatically applying brakes to individual wheels during instances of skidding. This intelligent system detects and reduces the loss of traction, which can occur in scenarios such as sudden swerving or on slippery roads. By selectively braking wheels, ESC helps drivers maintain control of their vehicles, significantly reducing the risk of accidents. The introduction of ESC has been a game-changer in automotive safety, leading to its widespread adoption and even becoming a mandatory feature in new vehicles in many countries. Its development marked a crucial step forward in the pursuit of safer driving experiences, potentially saving countless lives by improving a vehicle’s ability to navigate challenging road conditions.
4. Lane Departure Warning System (2000)

-
-
Inventor: Nick Parish (concept)
- First Commercial Use: Iteris for Mercedes Actros trucks
-
Purpose: Warns drivers when the vehicle drifts out of its lane without signaling.
-
The Lane Departure Warning System (LDWS), conceptualized by Nick Parish around the year 2000, represents a pivotal advancement in vehicular safety technology. Its primary purpose is to alert drivers when their vehicle unintentionally drifts out of its lane without the use of turn signals, thereby reducing the risk of accidents caused by driver inattention or drowsiness. The first commercial implementation of this system was by Iteris for Mercedes Actros trucks, marking a significant step forward in enhancing road safety for heavy-duty vehicles. By employing cameras and sensors to monitor lane markings on the road, the system provides visual, auditory, or tactile warnings to the driver, allowing them to correct their path promptly. Since its introduction, LDWS has become a standard feature in many modern vehicles, contributing to safer driving environments globally.
5. Blind Spot Detection (2004)

-
-
Manufacturer: Volvo
-
Purpose: Alerts drivers to vehicles in their blind spot, reducing risks during lane changes.
-
Blind Spot Detection, introduced by Volvo in 2004, represents a significant advancement in automotive safety technology, aimed at reducing the risks associated with lane changes. This system is designed to alert drivers to the presence of vehicles in their blind spots, areas that are often obscured from the driver’s direct line of sight despite the use of mirrors. By utilizing sensors and cameras strategically placed around the vehicle, Blind Spot Detection provides real-time feedback, typically through visual indicators or warning lights located on the side mirrors or pillars. This intuitive system helps drivers make safer decisions by increasing their awareness of surrounding traffic conditions, thereby minimizing the potential for accidents. As a pioneer in this technology, Volvo set a new standard for safety, influencing the broader automotive industry to adopt similar systems to enhance driver awareness and reduce collision risks.
6. Adaptive Cruise Control (1999)

-
-
Manufacturer: Mercedes-Benz (Distronic system)
-
Purpose: Maintains a safe distance from vehicles ahead by automatically adjusting speed.
-
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC), introduced by Mercedes-Benz in 1999 under the brand name Distronic, represents a significant advancement in automotive technology aimed at enhancing road safety and driving comfort. This intelligent system utilizes radar sensors to monitor the distance between the driver’s vehicle and the one in front. By automatically adjusting the car’s speed, ACC ensures that a safe following distance is consistently maintained, reducing the need for constant manual speed adjustments. This not only alleviates driver stress during long journeys or in heavy traffic but also contributes to overall road safety by minimizing the risk of rear-end collisions. The introduction of such technology marked a pivotal step towards the development of more sophisticated autonomous driving systems.
7. Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB) (2008)

-
-
Manufacturer: Volvo (introduced in the XC60)
-
Purpose: Applies brakes automatically when a collision is imminent.
-
Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB), first introduced by Volvo in their 2008 XC60 model, represents a significant advancement in vehicle safety technology. The primary purpose of AEB is to enhance driver safety by automatically applying the brakes if the system detects an imminent collision, thereby reducing the severity of impact or potentially avoiding the accident altogether. Utilizing a combination of sensors, cameras, and radar, AEB continuously monitors the vehicle’s surroundings, scanning for obstacles such as other vehicles, pedestrians, or even cyclists. When a potential collision is detected, the system warns the driver and, if no corrective action is taken, it promptly applies the brakes. This innovation not only minimizes the risk of accidents caused by human error or delayed reaction times but also underscores Volvo’s commitment to pioneering safety features that protect both occupants and other road users.
8. Pedestrian Detection System (2010)

-
-
Manufacturer: Volvo
-
Purpose: Identifies pedestrians in the vehicle’s path and brakes automatically to avoid collisions.
-
The Pedestrian Detection System, introduced by Volvo in 2010, marked a significant advancement in automotive safety technology. This innovative system was designed to enhance driver awareness and prevent accidents involving pedestrians. By using advanced radar and camera technology, the system could identify pedestrians in the vehicle’s path and automatically apply the brakes if a collision seemed imminent. This proactive approach aimed to reduce the number and severity of accidents, particularly in urban environments where pedestrian traffic is dense. Volvo’s commitment to safety and innovation was clearly demonstrated through this technology, setting a benchmark for other manufacturers to develop similar systems and furthering the evolution of intelligent, safety-focused vehicles.
The Road Ahead
These technologies represent more than just impressive feats of engineering—they are life-saving innovations reshaping how we think about mobility and safety. As artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking tools to emerge in the mission to eliminate road traffic accidents entirely.
If you’re passionate about traffic safety and want to stay informed on new innovations, follow our updates or consider partnering with organizations like NARTAP that are committed to accident prevention through technology.
Continue reading: Curious about how road infrastructure is evolving alongside vehicles? Click here to explore Infrastructure and External Safety Technologies →


